Differentiate X With Steps
Answer
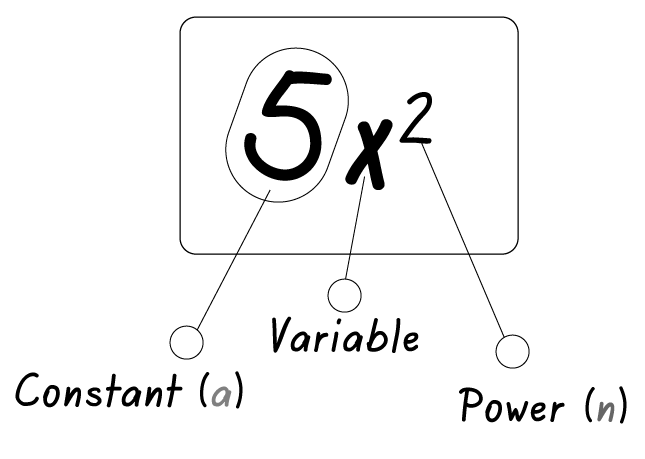
Differentiation of a variable, x
Differentiation of a variable "x" refers to the process of finding the rate of change of a function with respect to the variable "x." It involves determining the derivative of a function with respect to "x," which represents how the function changes as "x" changes. Differentiation is a fundamental concept in calculus, providing valuable insights into the behavior of functions and allowing us to analyze slopes, maxima, minima, and concavity. By understanding the differentiation of the variable "x," we can better comprehend the dynamics of functions and make predictions about their behavior.
Calculus solvers also solves expression in the following form:
Common functions
7
6x
x^{1/2}
2x^2
Exponential functions
-e^{-\frac{12}{7x}}
-3e^{2x}
Trigonometric functions
4 \sin (x)
-\cos(3x)
Logarithmic functions
4In9x
1. Find the derivative of the function -2x^{-\frac{1}{2}}.
Solution:
To find the derivative of a function in the form f(x) = ax^n, where a and n are constants, we use the power rule. The derivative is given by:
f'(x) = n \cdot a \cdot x^{n-1}.
Applying this rule to the given function, we have:
f'(x) = -\frac{1}{2} \cdot -2 \cdot x^{-\frac{1}{2}-1}</p><p>= x^{-\frac{3}{2}}.
Therefore, the derivative of -2x^{-\frac{1}{2}} is
x^{-\frac{3}{2}}.
2. Determine the derivative of e^{x}.
Solution:
The derivative of e^{x} is itself, as the derivative of
e^{x} is e^{x}.
This is a unique property of the exponential function e^{x}.
Therefore, the derivative of e^{x} is
e^{x}.
3. Calculate the derivative of 4\cos(9x).
Solution:
By applying the chain rule and derivative of cosine function, we have:
f'(x) = -4 \cdot 9 \sin(9x) = -36 \sin(9x).
Therefore, the derivative of 4\cos(9x) is
-36 \sin(9x).
4. Find the derivative of -3e^{\frac{8}{5}x}.
Solution:
Similarly to the derivative of e^{x}, the derivative of e^{\frac{8}{5}x} is itself times the constant \frac{8}{5}:
f'(x) = -3 \cdot \frac{8}{5} e^{\frac{8}{5}x} = -\frac{24}{5} e^{\frac{8}{5}x}.
Therefore, the derivative of -3e^{\frac{8}{5}x} is
-\frac{24}{5} e^{\frac{8}{5}x}.
5. Differentiate the function 4\sin(2x).
Solution:
Using the chain rule and derivative of the sine function, we get:
f'(x) = 4 \cdot 2 \cos(2x)= 8 \cos(2x).
Therefore, the derivative of 4\sin(2x) is
8\cos(2x).
1. \frac{d}{dx}\left(-2x^{-\frac{1}{2}}\right) = x^{-\frac{3}{2}}
2. \frac{d}{dx}\left(-e^x\right) = -e^x
3. \frac{d}{dx}\left(4\cos(9x)\right) = -36\sin(9x)
4. \frac{d}{dx}\left(-3e^{\frac{8}{5}x}\right) = -\frac{24}{5}e^{\frac{8}{5}x}
5. \frac{d}{dx}\left(5\ln x\right) = \frac{5}{x}
6. \frac{d}{dx}\left(2x^3\right) = 6x^2
7. \frac{d}{dx}\left(9e^{-2x}\right) = -18e^{-2x}
8. \frac{d}{dx}\left(7\sin(2x)\right) = 14\cos(2x)
9. \frac{d}{dx}\left(-4e^{5x}\right) = -20e^{5x}
10. \frac{d}{dx}\left(3\ln(4x)\right) = \frac{3}{x}
11. \frac{d}{dx}\left(-5\cos(3x)\right) = 15\sin(3x)
12. \frac{d}{dx}\left(6e^{-4x}\right) = -24e^{-4x}
13. \frac{d}{dx}\left(2\sin(5x)\right) = 10\cos(5x)
14. \frac{d}{dx}\left(8e^{2x}\right) = 16e^{2x}
15. \frac{d}{dx}\left(4\ln(3x)\right) = \frac{4}{x}
Sample Expressions
For best result write
1 as 1
-1 as -1
x as x
-x as -x
x^{1/2} as x^(1/2)
x^{-1/2} as x^-(1/2)
-x^{1/2} as - x^(1/2)
-x^{-1/2} as - x^-(1/2)
-2x as -2x
2x^2 as 2x^2
-2x^2 as -2x^2
2x^{1/2} as 2x^(1/2)
2x^{-1/2} as 2x^-(1/2)
-2x^{1/2} as -2x^(1/2)
-2x^{-1/2} as -2x^-(1/2)
2x^{-1} as 2x^-1
-2x^{-1} as -2x^-1
-x^{-1} as -x^-1
x^{-1} as x^-1
x^2 as x^2
-x^2 -x^2
-x^{-2} -x^-2
2x as 2x
e^x as e^x
-e^x as -e^x
-e^{-x} as -e^-x
e^{2x} as e^(2x)
e^{-2x} as e^-(2x)
-e^{2x} as -e^-(2x)
-e^{-2x} as e^-(2x)
e^{8/5x} as e^(8/5x)
e^{-8/5x} as e^-(8/5x)
-e^{8/5x} as -e^-(8/5x)
-e^{-8/5x} as -e^-(8/5x)
3e^x as 3e^x
3e^{-x} as 3e^-x
-3e^x as -3e^x
-3e^{-x} as -3e^-x
3e^{2x} as 3e^(2x)
3e^{-2x} as 3e^-(2x)
-3e^{2x} as -3e^(2x)
-3e^{-2x} as -3e^(-2x)
3e^{8/5x} as 3e^(8/5x)
3e^{-8/5x} as 3e^(-8/5x)
-3e^{8/5x} as -3e^(8/5x)
-3e^{-8/5x} as -3e^(-8/5x)
-\cos(x) as -cos(x)
4\sin(x) as 4 sin(x)
-\tan(3x) - tan(3x)
